Stapled Peptides
 Peptide-based therapeutics offer a viable solution since they are known to be potent and selective against biological targets that are otherwise difficult to manipulate with small molecules. Such approaches have been used to manipulate intracellular protein-protein interactions (PPIs), wherein large and shallow contact areas of a protein are successfully targeted by peptides, which are able to mimic the native counter protein. Although highly potent and selective, peptides often suffer from poor cell permeability, plasma stability and hence poor bioavailability. To overcome the poor pharmacokinetic properties of linear peptides, stapled peptides have been successfully developed and used to target intracellular PPIs. Indeed, an all-hydrocarbon stapled peptide, ALRN-6924, is under clinical development as an anti-cancer drug targeting HDM2/p53.
Peptide-based therapeutics offer a viable solution since they are known to be potent and selective against biological targets that are otherwise difficult to manipulate with small molecules. Such approaches have been used to manipulate intracellular protein-protein interactions (PPIs), wherein large and shallow contact areas of a protein are successfully targeted by peptides, which are able to mimic the native counter protein. Although highly potent and selective, peptides often suffer from poor cell permeability, plasma stability and hence poor bioavailability. To overcome the poor pharmacokinetic properties of linear peptides, stapled peptides have been successfully developed and used to target intracellular PPIs. Indeed, an all-hydrocarbon stapled peptide, ALRN-6924, is under clinical development as an anti-cancer drug targeting HDM2/p53.
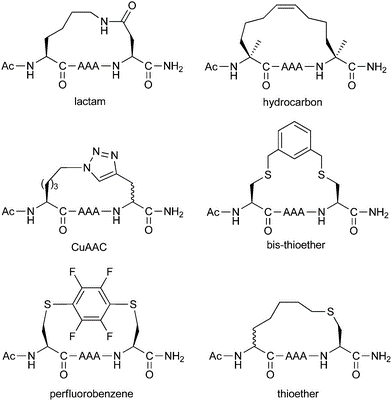
Different stapling chemistries have strengths and weaknesses in terms of both their synthetic ease and potential utility for addressing biological questions. To facilitate our clients’ research and project development, InnoPep is able to provide a comprehensive list of stapled peptides synthesis services, which includes: ring-closing metathesis, lactamization, click chemistry, and thioether formation.
1) Stapled Peptides Using Ring-Closing Metathesis
The all-hydrocarbon a-helix staple combines two distinct conformational stabilization strategies to induce a-helical structure, namely, a,a-disubstitution and macrocyclic bridge formation. Three different types of all hydrocarbon staples are shown in the figure, demonstrating the creation of a stabilized α-helix in a peptide. Approximately one turn of the helix would be i and i+3 (or i, i+4) and two turns of the helix would be i, i+7; three turns of the helix would be i, i+11. During solid-phase peptide synthesis, a-methyl, a-alkenylglycine cross-linking amino acids are incorporated in appropriate positions. An i, i+3 stapled peptide requires one unit of R5 at the i position and one unit of S5 at the i+3 position. An i, i+4 stapled peptide requires two units of S5 incorporated at the relative positions i and i+4. An i, i+7 stapled peptide requires one unit of R8 at the i position and one unit of S5 at the i+7 position. Resin-bound peptide is treated with Grubbs I olefin metathesis catalyst to produce a cross-link between the two non-natural amino acids, resulting in a stapled peptide that is braced in a a-helical conformation.
2) Stapled Peptides using Click Chemistry
The high efficiency and mild conditions of “click” reaction (Copper catalyzed Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction) combined with the ease of synthesis of the necessary unnatural amino acids allows for facile synthesis of triazole-stapled peptides. For example, a combination of L-Nle(εN3) and D-Pra (D-Propargylalanine) substituted at the i and i+4 positions can be used for the generation of single triazole-stapled peptides.


Stapled peptides have been studied in the targeting of several proteins which are relevant in Cancer, Diabetes, HIV, Atherosclerosis etc. These include proteins such as BCL-2, BCL-XL, BAX, MCL-1, glucokinase, hDM2, hDMX, NOTCH/CSL, HIV-1 capsid, HIV-1 gp41, ABCA1 and Estrogen receptor.
Advantages of Stapled Peptides
- Better target affinity
- Increased proteolytic resistance and serum half-life
- Cell penetration through endocytic vesicle trafficking
- Target either extracellular or intracellular proteins
- Disrupt Protein-Protein interactions
- Non-immunogenic
- Viable pharmacokinetics and in vivo stability
References
- Jackson DY, King DS, Chmielewski J, Singh S, & Schultz PG (1991) General approach to the synthesis of short alpha-helical peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113(24):9391-9392.
- Walensky LD, et al. (2004) Activation of apoptosis in vivo by a hydrocarbon-stapled BH3 helix. Science 305(5689):1466-1470.
- Chang YS, et al. (2013) Stapled alpha-helical peptide drug development: A potent dual inhibitor of MDM2 and MDMX for p53-dependent cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(36):E3445-E3454.
- Walensky LD & Bird GH (2014) Hydrocarbon-stapled peptides: principles, practice, and progress. J. Med. Chem. 57(15):6275-6288.
